Vancouver Referencing | A Quick Guide & Reference Examples
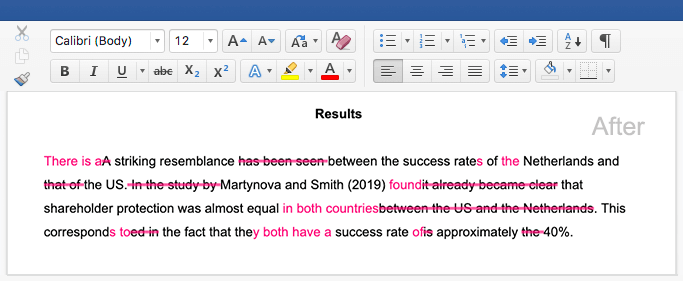
Vancouver is a system of referencing commonly used in biomedicine, among other scientific disciplines. In Vancouver style, you place a reference number in the text wherever a source is cited:
This number corresponds to an entry in your reference list – a numbered list of all the sources cited in your text, giving complete information on each:
This quick guide presents the most common rules for Vancouver style referencing. Note that some universities and journals have their own guidelines for the formatting of Vancouver references.
Vancouver in-text citations
In Vancouver style, citations are marked in your text with numbers. These numbers appear either in parentheses or in superscript – choose one option and stick to it consistently:
| Parentheses numbering | Superscript numbering |
|---|---|
| Levitt (2) argues that … | Levitt2 argues that … |
The numbers usually appear after the name of the author or after a direct quote. They may also appear at the end of the sentence:
Naming authors
You will often need to mention the author when referring to a work or introducing a quote. Only use the author’s last name in your text. If a source has multiple authors, name only the first author followed by ‘et al.’:
It’s not always necessary to mention the author’s name in your text – but always include the reference number when you refer to a source:
Numbering references
Sources are numbered based on the order in which they are cited in the text: the first source you cite is 1, the second 2, and so on.
If the same source is cited again, use the same number to refer to it throughout your paper. This means that the numbers might not appear in consecutive order in your text:
Citing multiple sources
You can also cite multiple sources in the same place:
To cite several sources that appear consecutively in your numbered list, you can use an en dash to mark the range.
In this case, the citation refers the reader to sources 1, 4, 5, 6, and 7.
Citing page numbers
You must specify a page number or range when you directly quote a text, and it can be helpful to do so when you are paraphrasing a particular passage.
Place the page number after the reference number inside the same parentheses, preceded by ‘p.’:
If you’re using superscript numbers, the page number also appears in superscript, in parentheses after the reference number:
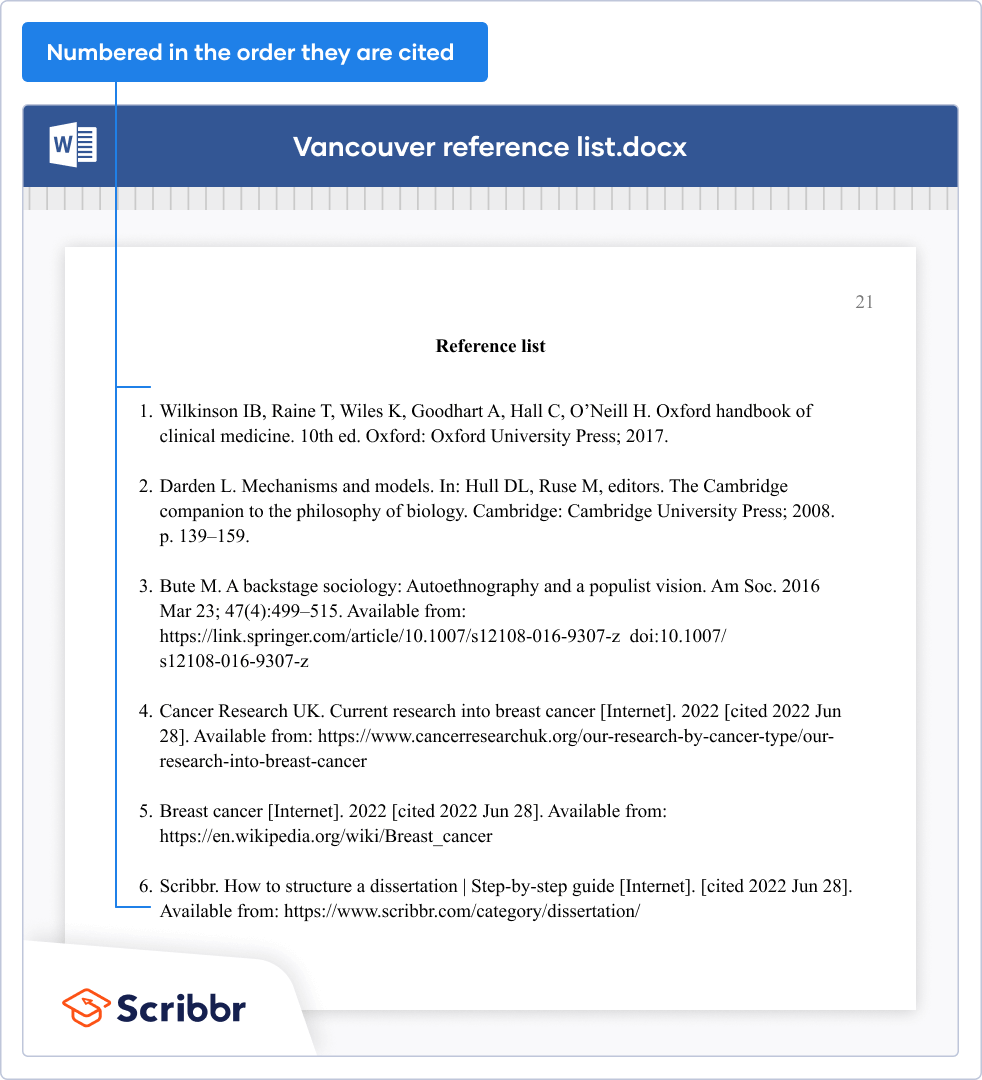
Creating a Vancouver reference list
Your reference list is where you provide the information your readers will need in order to look up the sources cited in your text. It consists of a numbered list of all your sources, providing key information including the author, title and publication date of each source.
The list appears in numerical order at the end of your paper. Each entry ends with a full stop, unless the last element is a DOI or URL.
Vancouver reference list example
Author names
Each entry starts with the author’s last name and initials.
When a source has more than one author, their names are separated by commas. If a source has more than six authors, list the first six followed by ‘et al.’
| 1 author | Shields G. |
|---|---|
| 2–6 authors | Johnson FH, Singh J. |
| 7+ authors | James F, Pieters J, Deptford G, Harrison R, Bregman E, Empson A, et al. |
Source titles
Only the first word of the title and subtitle, along with any proper nouns, are capitalised:
Titles in Vancouver referencing are consistently written in plain text. Do not use italics or quotation marks.
Vancouver reference examples
The information you provide differs according to the type of source you’re citing, since different details are relevant in different cases. Formats and examples for the most commonly cited source types are given below.
| Format | x. Author(s). Title. Edition. Place of publication: Publisher; Year. |
| Example | 1. Wilkinson IB, Raine T, Wiles K, Goodhart A, Hall C, O’Neill H. Oxford handbook of clinical medicine. 10th ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2017. |
| Notes |
|
| Format | x. Author(s). Title of chapter. In: Editor(s), editors. Title of book. Place of publication: Publisher; Year. Page range. |
| Example | 2. Darden L. Mechanisms and models. In: Hull DL, Ruse M, editors. The Cambridge companion to the philosophy of biology. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2008. p. 139–159. |
| Notes |
|
| Format | x. Author(s). Article title. Journal Name (abbreviated). Year Month Day; Volume(Issue):page range. Available from: URL DOI |
| Example | 3. Bute M. A backstage sociologist: Autoethnography and a populist vision. Am Soc. 2016 Mar 23; 47(4):499–515. Available from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12108-016-9307-z doi:10.1007/s12108-016-9307-z |
| Notes |
|
| Format | x. Author(s). Title [Internet]. Year [cited Date]. Available from: URL |
| Example | 4. Cancer Research UK. Current research into breast cancer [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2020 Feb 14]. Available from: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/our-research/our-research-by-cancer-type/our-research-into-breast-cancer/current-breast-cancer-research |
| Notes |
|
Missing information in Vancouver references
Some sources will be missing some of the information needed for a complete reference. See below for how to handle missing elements.
No author
As shown in the website example above, when no individual author is named, you can usually name the organisation that produced the source as the author.
If there is no clear corporate author – for example, a wiki that is created and updated collaboratively by users – you can begin your reference with the title instead:
No date
Sources such as websites may lack a clear publication date. In these cases you can omit the year in your reference and just include the date of your citation:
No page numbers
You may want to show the location of a direct quote from a source without page numbers, such as a website. When the source is short, you can often just omit this, but where you feel it’s necessary you can use an alternate locator like a heading or paragraph number:
Frequently asked questions about Vancouver referencing
- What’s the difference between Harvard and Vancouver referencing styles?
-
Harvard referencing uses an author–date system. Sources are cited by the author’s last name and the publication year in brackets. Each Harvard in-text citation corresponds to an entry in the alphabetised reference list at the end of the paper.
Vancouver referencing uses a numerical system. Sources are cited by a number in parentheses or superscript. Each number corresponds to a full reference at the end of the paper.
Harvard style Vancouver style In-text citation Each referencing style has different rules (Pears and Shields, 2019). Each referencing style has different rules (1). Reference list Pears, R. and Shields, G. (2019). Cite them right: The essential referencing guide. 11th edn. London: MacMillan. 1. Pears R, Shields G. Cite them right: The essential referencing guide. 11th ed. London: MacMillan; 2019. - When should I use an in-text citation in Vancouver style?
-
A citation should appear wherever you use information or ideas from a source, whether by quoting or paraphrasing its content.
In Vancouver style, you have some flexibility about where the citation number appears in the sentence – usually directly after mentioning the author’s name is best, but simply placing it at the end of the sentence is an acceptable alternative, as long as it’s clear what it relates to.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, August 19). Vancouver Referencing | A Quick Guide & Reference Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 9 December 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/referencing/vancouver-style/